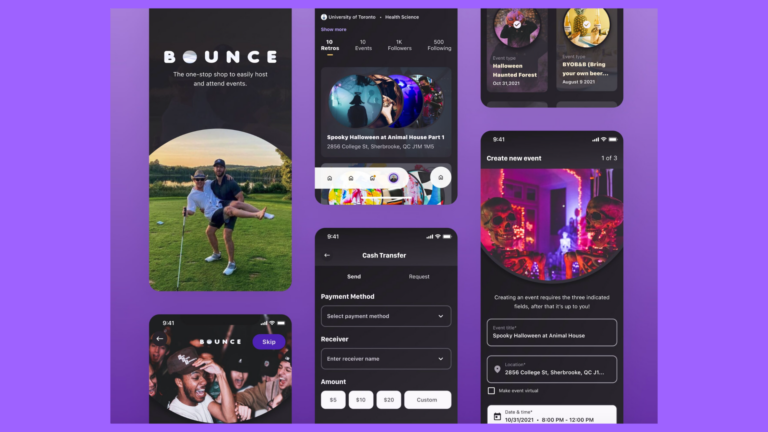
You’re about to build your brand. It’s exciting, a little frightening, and definitely overwhelming. There are too many variables to think of, but one thing’s for sure—you’ll need a website to put your product on the map.
It’s no easy task, either. Your website will be a first impression for the majority of your potential customers, who are mostly digital natives. You know you’ll be needing spotless UX and UI design, but the question is: are you creating a website or a web application?
@weareproduktiv Website or Web Application? Web sites and web applications require different approach and process. You wouldn’t build a custom home without hiring an architect. So why would you build a custom application without hiring a designer? Founder and CEO Justin Wood speaks on it! 👀 P.S. Notice anything different about us?? Stay tuned for more on THAT! #rebrand ♬ original sound - Produktiv | Digital Agency
As an end user, knowing the difference between a website and a web application is rarely a top priority, but if you’re about to build one, knowing what each one can do and how they’re built will matter, a lot. Not only do they involve very different UX and UI design requirements, they also offer completely different experiences that can make or break the product you’re selling.
To keep things simple, we’ve broken down all the major differences between a website and a web application so you know which one you’ll be needing for your brand.
Websites vs. Web Applications: What’s The Difference, Anyway?
Websites Are Showcases That Funnel
You know what a website is. They’re navigable web pages with pretty images, videos, other digital content, and maybe even background music that makes you press “mute” on your computer.
Unlike web applications, websites are static, one-way informational feeds with content that’s not dynamically updated. They’re usually built with HTML, CSS, or if it’s feeling fancy, some JavaScript as well.
While all (good) modern websites include some level of interactivity (think: hover effects, fun cursors, scroll effects), the user can’t really affect what’s being displayed. There are many instances where a website will include web application elements like Google Maps widgets or Calendly plugins, but the main body of it will still remain largely static.
On the most basic level, you can think of websites as a showcase or gallery of your content, but it doesn’t have to stop there. The websites designed by Produktiv, for instance, use the right combination of UX design and UI components to turn a “showcase” into a strong marketing funnel that taps right into any business’s ideal customer base.
[Create Your Marketing Funnel]
Depending on what you’re selling, a well-designed website can make a powerful statement. In today’s world, however, many users expect to interact with pages that “do it all.” That’s exactly where a web application can make a difference.
Web Applications Are Meaningful Interactions
Whereas websites convey the information potential customers need to know before making their decision, web applications have features that they can return to again and again.
We mentioned earlier that modern websites can contain interactive UI elements in the form of widgets and plugins, but their main body will be static content. A web application, on the other hand, will have interaction as its core functionality.
Web application interactions can take place in the form of a downloadable, a live chat box, a user login function, or online payment like e-commerce sites.
On a daily basis, the modern internet surfer will interact with countless web applications, including social media, online shopping, food delivery services, hotel and flights booking applications, and even text-heavy sites like Wikipedia, which gives any user access to their content editor.
[Start Building Your Web Application]
Do You Need A Website Or A Web Application?
So—do you need to build a website or a web application? We’ll keep it simple for you. Ask yourself these three questions:
- Will I be collecting data from my users?
- Will people be logging in to an account?
- Is there a need for a mobile app in the future?
If you answered “yes” to any of the above, then it’s a web application you need. Why? Collecting data and creating accounts are more advanced features that need to be built like a web application, especially if you’d like the option to eventually turn your website into a mobile app.
With a smart UX/UI architect, web applications are easily maintainable, updatable, and customizable. You can also keep your data securely tucked away in a cloud storage and retrieve it whenever you need.
Short answer: websites are effective, straightforward information and marketing funnels, but web applications can do all the same things with additional future-proof features built right into its architecture.
Websites vs. Web Applications: Comparison Chart
| Websites | Web Applications |
| Static, informative | Dynamic, interactive |
| Has some interactive elements (widgets, plugins) | Entirely based on interactions |
| Piques curiosity to inspire action | Practical features, dialogs with the user |
| Created with HTML, CSS, JavaScript | Built with PHP, Ruby, Python, HTML, CSS, JavaScript |
Do Your User Research
Done right, websites can be enough to represent your brand and get the right customers in the door. Even without the practical interactions that web applications have, a good website with the right UX and UI design becomes a powerful storytelling tool to pique interest and inspire action.
For web applications, implementing well-researched UX and UI design is doubly important. After all, its main purpose is to make it enjoyable for the user to interact with everything on your page.
No matter which type of page you decide to build, what you want to end up with is a memorable experience from the user’s perspective. What does your audience want that’s missing from the digital landscape? How comfortable are they with technology? What do you want them to do with your page?
We know the planning stage is the hardest and least fun, but trust us—it’s the most important one.
See How It’s Done
The best websites and web applications involve hard work and ingenuity, and they’re not projects that can be tackled in a day. Take the time to find UX and UI designers, copywriters, and developers you can trust—the right team can take your product from zero to one.
Think about it. You wouldn’t build a custom home without hiring an architect, so why would you build a website or custom application without hiring a web design team?
At Produktiv, we create digital presences with clear overarching goals: drive ambitious growth and happy conversions. With a full team of UX/UI professionals, growth marketing strategists and clever creatives, we’ve got the ultimate playbook to help you win.
[Talk To Our Design Team]
Bonus: Download Our Custom UX Audit Template
To get you started on the right foot, we’ve put together a comprehensive UX Audit Template so you can identify exactly what your website or web application is missing, and how to take it to the next level.
[Get Our Free UX Audit Template]